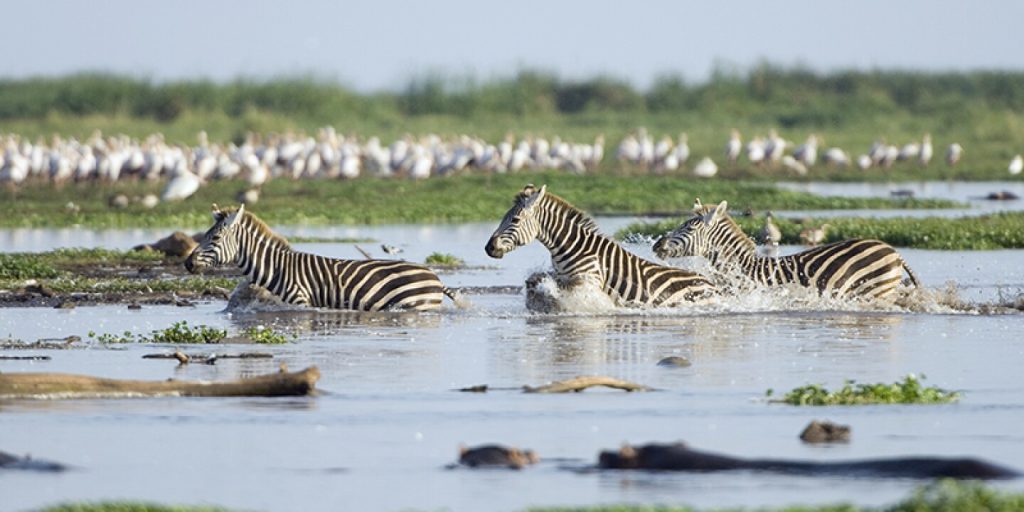
Kilimanjaro is one of the most majestic mountains in the world. It is also one of the most accessible peaks, with a wide variety of trails and routes for climbers and visitors to explore. But the mountain is more than just a tourist attraction – it is also a vital source of information about the environment, geology, and climate of the region. In recent years, scientists have used mapping to better understand the mountain and its surrounding ecosystems, revealing valuable insights that will help protect the area for generations to come.
Exploring the Beauty of Kilimanjaro
Kilimanjaro stands tall over Tanzania, reaching an impressive 19,341 feet above sea level. The mountain is made up of three distinct volcanic cones: Kibo, Shira, and Mawenzi. Due to its unique location near the equator, Kilimanjaro’s climate and vegetation changes as you go up in elevation. The lower slopes include lush rainforests, while the summit offers a breathtaking view of snow-capped peaks and glaciers. Hikers can traverse the mountain in anywhere from three to nine days, depending on the route chosen.
On the human side, Kilimanjaro is known for its vibrant and diverse culture. The mountain is the traditional home of the Chagga people, who have lived in the area for centuries and rely on the mountain’s resources for their livelihood. The area is also a popular spot for adventurers, with an impressive array of hiking and climbing routes.
Mapping a Majestic Mountain
In recent years, scientists have used mapping to better understand the mountain and its surrounding ecosystems. This type of research can provide valuable insights into the physical and biological processes of the mountain. For example, satellite imaging can be used to study the mountain’s glaciers, which are vital indicators of the region’s climate. Researchers have also used mapping to track changes in vegetation cover, soil erosion, and surface water runoff.
Mapping can also help identify potential threats to the mountain. In the past, deforestation and overgrazing have caused significant damage to the mountain’s ecology. By analyzing satellite data, scientists can identify areas where these activities are taking place, and take steps to protect them.
More broadly, mapping can help scientists better understand the mountain’s ecosystems, and provide information that can be used to protect the mountain for future generations. As the world’s tallest free-standing mountain, Kilimanjaro is a vital source of information about the environment, geology, and climate of the region.
Kilimanjaro is an iconic mountain with immense cultural and ecological significance. By using mapping technology, scientists can better understand the mountain and its surrounding ecosystems, providing valuable insights that can help protect the area for generations to come. Whether you’re an adventurer or a scientist, one thing’s for sure: Kilimanjaro is a magnificent mountain to explore.